In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in various fields, and scientific writing is no exception. Researchers have been using AI-powered tools to assist in their research and writing processes, and one such tool that has gained popularity is ChatGPT.
ChatGPT, or Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer, is a language model developed by OpenAI that uses deep learning to generate human-like text. It has been used in various applications, such as chatbots and text completion, but its use in scientific writing has been on the rise.
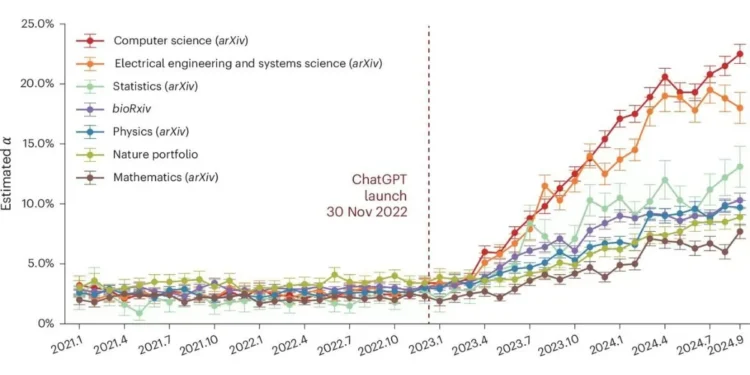
A recent study conducted by researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Chicago has shed light on the increasing use of ChatGPT in scientific writing. The study analyzed over a million papers from various fields, including computer science and competitive research, and found a significant pattern in the use of ChatGPT.
According to the study, there has been a steady increase in the use of ChatGPT in scientific writing, with a particular surge in the past two years. The researchers also found that the use of ChatGPT was more prevalent in computer science and competitive research fields, where the demand for quick and accurate results is high.
One of the most interesting findings of the study was the link between author habits and the use of ChatGPT. The researchers found that authors who used ChatGPT in their writing tended to have a higher number of publications and citations compared to those who did not use the tool. This suggests that ChatGPT is not only helping researchers in their writing process but also improving the quality and impact of their work.
The study also revealed a correlation between paper length and the use of ChatGPT. It was found that longer papers tend to have a higher percentage of text generated by ChatGPT. This could be due to the time-saving aspect of the tool, as it can quickly generate text based on the input provided by the author.
Moreover, the study also looked at the geographical distribution of ChatGPT usage in scientific writing. It was found that the use of ChatGPT was more prevalent in countries with a higher number of English-speaking researchers, such as the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada. This could be attributed to the fact that ChatGPT is trained on a large dataset of English text, making it more suitable for use by English-speaking researchers.
The findings of this study have raised broader discussions about the role of AI in research and the integrity of scientific writing. Some argue that the use of AI in research could lead to a decline in the quality and originality of scientific work. However, others believe that AI-powered tools like ChatGPT can assist researchers in their work and improve the efficiency and accuracy of their results.
One of the main concerns raised by critics is the potential for plagiarism when using AI-powered tools. However, the researchers behind this study have addressed this issue by stating that ChatGPT is not designed to replace human writing but rather to assist in the writing process. They also suggest that proper citation and credit should be given to the tool when used in research papers.
The use of AI in research is still a relatively new concept, and it is essential to have discussions and debates about its impact on the integrity of scientific writing. However, it is undeniable that AI-powered tools like ChatGPT have the potential to revolutionize the way researchers work and produce their findings.
In conclusion, the use of ChatGPT in scientific writing has seen a significant increase in recent years, with patterns linked to author habits, paper length, and geography. While there are concerns about the role of AI in research, the findings of this study suggest that ChatGPT can be a valuable tool for researchers, improving the quality and impact of their work. As AI continues to advance, it is crucial for the scientific community to embrace its potential and use it responsibly to further our understanding of the world.