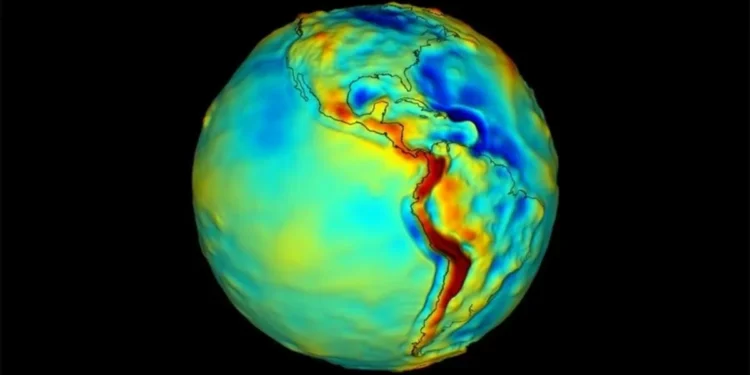
NASA, in collaboration with academia and private companies, is on the verge of a groundbreaking development that could revolutionize our understanding of Earth’s gravity and pave the way for future space exploration. The space agency, known for its pioneering missions and cutting-edge technology, is working on the first quantum sensor to map Earth’s gravity from space.
This innovative instrument, which uses cold rubidium atoms, is compact yet highly sensitive, and is set to deliver long-term measurements of Earth’s gravity. This mission has the potential to transform the way we study Earth’s subsurface and explore other planetary bodies in our solar system.
The concept of mapping Earth’s gravity from space is not new. In fact, NASA has been using satellites to measure gravity for decades. However, these traditional methods have limitations, such as being affected by Earth’s rotation and other external forces. This is where the quantum sensor comes in. By using cold rubidium atoms, which are cooled to near absolute zero, this sensor can detect the tiniest changes in gravity, providing more accurate and precise measurements.
The development of this quantum sensor is a result of a collaboration between NASA, academia, and private companies. This partnership brings together the expertise and resources of different sectors, making it possible to achieve something that would have been impossible for a single entity to accomplish.
The potential applications of this quantum sensor are vast. One of its main uses will be in mapping Earth’s subsurface, which has always been a challenge for scientists. By measuring gravity variations, the sensor can provide valuable insights into the composition and structure of Earth’s interior. This will not only enhance our understanding of the planet, but also aid in the detection of underground resources such as oil, gas, and minerals.
Moreover, this technology can also be used to study other planetary bodies in our solar system. By mapping their gravity, we can gain a better understanding of their composition and evolution. This will be crucial for future space missions, as it will help in identifying potential landing sites and determining the best approach for exploration.
The compact size of this quantum sensor is another advantage. Traditional gravity mapping instruments are bulky and require a lot of power, making it difficult to send them into space. However, the quantum sensor is small and lightweight, making it easier to launch into orbit. This means that it can be placed on smaller satellites, making it more cost-effective and accessible for future missions.
The potential impact of this mission goes beyond just Earth and our solar system. The development of this quantum sensor could also have implications for future space exploration beyond our solar system. By accurately measuring gravity, we can better understand the gravitational pull of other planets and stars, which is crucial for navigating through space.
This mission also highlights the importance of investing in cutting-edge technology and pushing the boundaries of what is possible. NASA has always been at the forefront of innovation, and this collaboration with academia and private companies is a testament to their commitment to pushing the limits of space exploration.
The development of this quantum sensor is a significant step towards unlocking the mysteries of our planet and the universe. It has the potential to transform our understanding of Earth’s subsurface and pave the way for future space exploration. This mission is a testament to the power of collaboration and the endless possibilities that can be achieved when different sectors come together to work towards a common goal.
In conclusion, NASA’s collaboration with academia and private companies to develop the first quantum sensor to map Earth’s gravity from space is a groundbreaking achievement that has the potential to transform our understanding of our planet and the universe. This mission is a shining example of the power of innovation and collaboration, and it is an exciting time for space exploration. We can’t wait to see the groundbreaking discoveries that this quantum sensor will uncover.