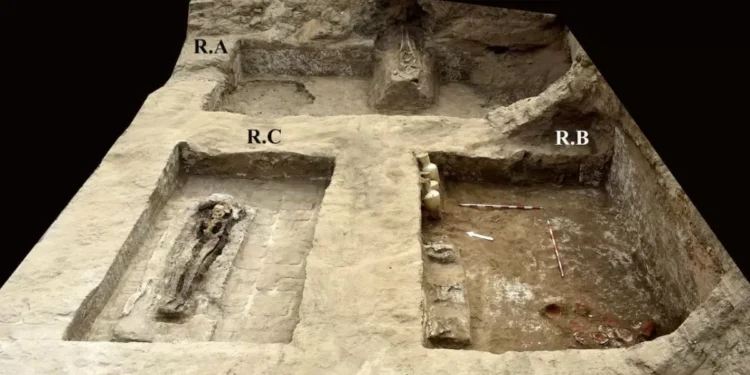
In a remarkable discovery, archaeologists have uncovered a 3,200-year-old tomb at Tell el-Maschuta in northeastern Egypt. The tomb, believed to have belonged to a high-ranking official, is a testament to the rich history and culture of this ancient civilization.
Located near the Nile Delta, Tell el-Maschuta has long been a site of interest for archaeologists due to its strategic location and its significance as a center of trade and commerce in ancient Egypt. However, the recent discovery of this tomb has shed new light on the area, providing a deeper understanding of the people and their way of life.
The tomb, which has been dated to the New Kingdom period (1550-1070 BCE), consists of a burial chamber and three adjoining rooms. The chamber itself is beautifully decorated with colorful paintings depicting scenes from the afterlife, including the journey of the deceased in the underworld.
But it is not just the stunning artwork that has caught the attention of experts. The tomb also contains a number of artifacts, including a gold ring inscribed with the name of Ramesses III, one of the most powerful pharaohs of the New Kingdom period. This is a significant discovery as it provides evidence of the tomb’s owner being closely associated with the ruling king.
In addition, the tomb also holds bronze arrowheads, pottery inscriptions, and other objects that provide valuable insight into the practices and beliefs of the ancient Egyptians. Particularly interesting is the discovery of pottery inscriptions referring to Horemheb, the last pharaoh of the 18th dynasty, which suggest that the tomb may have been reused and expanded upon during different periods.
This discovery is a testament to the skilled craftsmanship and advanced technology of the ancient Egyptians. The intricate paintings and inscriptions, as well as the sophisticated architecture of the tomb, are a testament to their ingenuity and dedication to preserving the memory of their deceased.
The discovery of this tomb at Tell el-Maschuta is a groundbreaking one and adds to the growing body of knowledge about the ancient civilization that once thrived in this region. It not only provides a glimpse into the lives of the elite class of ancient Egypt but also sheds light on the burial practices and beliefs of the society.
Furthermore, the discovery of this tomb also highlights the importance of continued excavation and research at Tell el-Maschuta and other sites in the region. It is through such discoveries that we are able to deepen our understanding of the past and gain valuable insights into the lives of our ancestors.
The excavation of this tomb is a collaborative effort between the Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities and a team of international archaeologists. Their dedication and hard work have undoubtedly paid off, as this discovery adds to the already rich cultural heritage of Egypt and further solidifies its place as a cradle of civilization.
As we continue to uncover the mysteries of the past, we are reminded of the significance of preserving our cultural heritage. This discovery at Tell el-Maschuta serves as a reminder of the importance of protecting and safeguarding our ancient sites, not only for the benefit of future generations but also for the sake of our own understanding of the world and its history.
In conclusion, the discovery of a 3,200-year-old tomb at Tell el-Maschuta in northeastern Egypt is a significant achievement in the field of archaeology. It not only provides valuable insights into the lives of the ancient Egyptians but also serves as a reminder of the rich cultural heritage of this ancient civilization. This discovery is a testament to the dedication and perseverance of archaeologists and their determination to uncover the secrets of the past.